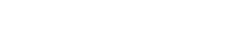Sebaceous Hyperplasia
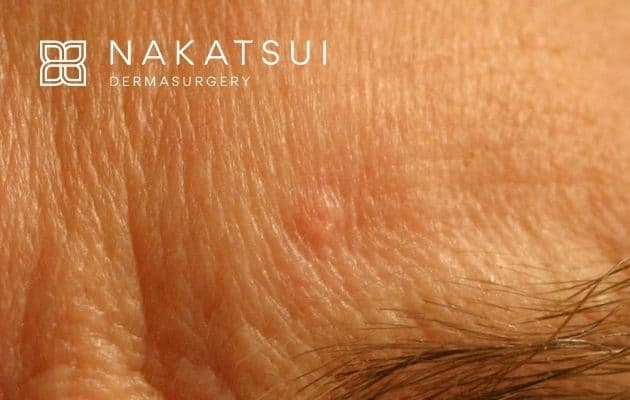
What is a Sebaceous Hyperplasia?
A sebaceous hyperplasia is a benign skin lesion that becomes more common with age. It’s caused when your sebaceous oil glands produce too much oil, which can be trapped under your skin and cause bumps.1
They are common, harmless skin growths that usually appear in adult life. Sebaceous hyperplasia are primitive oil gland growths that are much like icebergs; that is, we see the top part of them, but they are considerably larger under the skin. They never become malignant. The lesions begin as slightly raised, yellowish or milky coloured lesions with a central dimple, giving them a crater-like appearance. Gradually they thicken and become larger. They are not dangerous and do not require treatment, although we treat many patients for these lesions if they do not like the appearance of them. Some people are fortunate but others can can develop many on their face through no fault of their own.
What do they look like?
They are typically 2-5 mm in diameter and may be flesh-coloured or slightly yellow. Patients with many of these typically will have an oily complexion. On occasion, they can look very similar to basal cell carcinoma. If you’re concerned about the appearance of any spots on your skin, you should talk to your dermatologist.
Important to know: It may also be difficult to distinguish the condition from acne. The two conditions may appear similar, but a whitehead or blackhead due to acne will usually have a raised centre, whereas bumps from sebaceous hyperplasia will be indented. These bumps are typically small and cause no pain.
What causes Sebaceous Hyperplasia?
Enlarged sebaceous glands cause sebaceous hyperplasia. These glands become enlarged when the cells that form the gland, known as sebocytes, overgrow and overproduce sebum. This leads to a buildup of oil.
Prevention
There is no way to prevent these benign yet common lesions. However, a person may be able to reduce the appearance of any bumps that appear.
It is also important to note that exposure to UV rays is considered a cofactor. To reduce their exposure to UV rays, a person can reduce the amount of time they spend in direct sunlight and protect their skin with sunscreen.
That said, they can still occur in skin with very little UV exposure.2
How are Sebaceous Hyperplasia treated?

Our newest treatment uses billionths of a second pulses of electricity to eradicate these benign growths
Sebaceous hyperplasia treatment consists or removing them or vaporizing them with a carbon dioxide resurfacing laser or nanosecond pulsed electric field treatments (CellFX). After treatment, the treatment sites are raw and red. It may take several months for the redness to fade. After seven days, make-up can be applied to cover the redness until it fades. Lesions may rarely return or push to the surface requiring another treatment. In general, they are not treated by excision because they might leave an unsightly scar. Electrodessication can also be tried but CellFX or the carbon dioxide laser is a more precise method of ablating these benign yet common skin lesions.
Other traditional treatments include cryosurgery, electrodessication, curettage, topical trichloroacetic/bichloroacetic acid and shave excision.

Sebaceous Hyperplasia Treatments
CellFX co2 laser1 https://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/what-is-sebaceous-hyperplasia-treatment
2 https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321550#causes